Coronary Arteries/Right Coronary Artery
The right coronary artery (RCA) arises at the right aortic sinus and courses in the coronary (AV) groove between the right atrium and ventricle.
At the level of the right auricular appendage, it gives off the SA nodal branch, which ascends to the junction of the SVC with the right atrium, where the SA node is located. As it reaches the inferior margin of the heart in the coronary groove, it will usually give off a right marginal branch that supplies the right ventricle along the inferior border. The RCA then curves around the inferior margin of the heart in the coronary groove onto the inferior and posterior surfaces of the heart, passing somewhat to the left toward the junction with the posterior interventricular groove, also called the crux of the heart. At the crux, the AV nodal branch passes deep into the interatrial septum to supply the AV node. The RCA divides into a larger posterior interventricular artery, which descends in the groove or sulcus of the same name. It passes toward but typically does not reach the apex of the heart. It supplies the right and left ventricles and posterior portions of the interventricular septum. A small branch continues to the left side of the heart to supply portions of the left atrium and ventricle and will anastomose with the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery (LCA) (see Figures 16-1 and 16-2).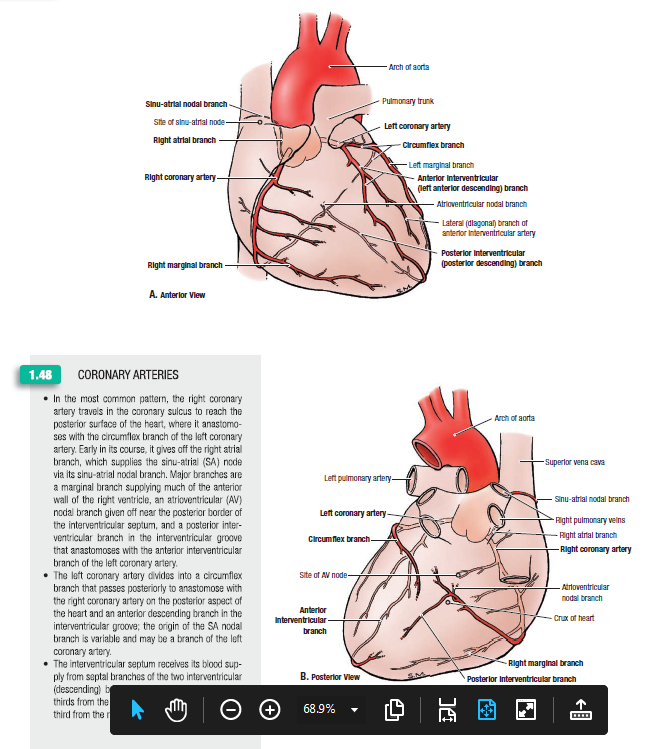
The right coronary artery (RCA) arises at the right aortic sinus.
TIt courses in the coronary (AV) groove between the right atrium and ventricle to reach the posterior .
At the level of the right auricular appendage, it gives off the SA nodal branch, which ascends to the junction of the SVC with the right atrium, where the SA node is located. As it reaches the inferior margin of the heart in the coronary groove, it will usually give off a right marginal branch that supplies the right ventricle along the inferior border. The RCA then curves around the inferior margin of the heart in the coronary groove onto the inferior and posterior surfaces of the heart, passing somewhat to the left toward the junction with the posterior interventricular groove, also called the crux of the heart. At the crux, the AV nodal branch passes deep into the interatrial septum to supply the AV node. The RCA divides into a larger posterior interventricular artery, which descends in the groove or sulcus of the same name. It passes toward but typically does not reach the apex of the heart. It supplies the right and left ventricles and posterior portions of the interventricular septum. A small branch continues to the left side of the heart to supply portions of the left atrium and ventricle and will anastomose with the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery (LCA).
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
The right coronary artery supplies the right side of the heart and provides some perfusion to the inferior aspect of the left ventricle through its continuation as the right posterior descending artery.
The right coronary artery arises from the aorta, superior to the right cusp of the aortic valve. It begins between the root of the pulmonary trunk and the right auricle then courses in the coronary (AV) groove between the right atrium and ventricle.
At the level of the right auricular appendage, it gives off the SA nodal branch, which ascends to the junction of the SVC with the right atrium, where the SA node is located. As it reaches the inferior margin of the heart in the coronary groove, it will usually give off a right marginal branch that supplies the right ventricle along the inferior border. The RCA then curves around the inferior margin of the heart in the coronary groove onto the inferior and posterior surfaces of the heart, passing somewhat to the left toward the junction with the posterior interventricular groove, also called the crux of the heart. At the crux, the AV nodal branch passes deep into the interatrial septum to supply the AV node. The RCA divides into a larger posterior interventricular artery, which descends in the groove or sulcus of the same name. It passes toward but typically does not reach the apex of the heart. It supplies the right and left ventricles and posterior portions of the interventricular septum. A small branch continues to the left side of the heart to supply portions of the left atrium and ventricle and will anastomose with the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery (LCA)
The right coronary artery gives rise to the following branches:
- Posterior descending artery. Supplies the inferior wall, posterior interventricular septum, and the posteromedial papillary muscle. In a few cases, the circumflex artery gives off the posterior descending artery.
- Right marginal artery. Supplies the right ventricular wall.
- SA nodal artery. Passes between the right atrium and the opening of the superior vena cava and supplies the SA node. In a few cases, the circumflex artery supplies the SA nodal artery.
Coronary Dominance
Coronary dominance is determined by which of the left and right coronary arteries gives rise to the posterior interventricular artery, which supplies the posterior interventricular semptum and part of the left ventricle. The dominant artery is usually the right coronary artery.
- In a balanced coronary circulation, the conduction system nodes of the heart (SA and AV nodes) are typically supplied by the RCA.
- In a balanced coronary circulation, the anastomoses between branches of the RCA and LCA occur at the posterior coronary and posterior interventricular grooves.
As a cardiologist, you are concerned about blockage of the artery to the SA node in a patient. This artery typically arises from which of the following?